Introduction
Learn About Git and Github
GitHub is a code hosting platform for collaboration using the Git Version Control System. In layman’s terms, it is the place where you keep all your projects and multiple people can work together on those projects.
Good resources to get started with GitHub:
- GitHub Learning Lab
- Git & GitHub Crash Course For Beginners - Traversy Media
- Git and GitHub crash course from FreeCodeCamp
Note that you do not need to be a master in VCS/Git/GitHub to start contributing. Once you are comfortable with the basics, you can start contributing.
Process
Getting Started with project
Step 1: Fork the Repository you want to work on. GitHub will create a new repository in your profile so that you can clone it into your local system to make changes.

Step 2: Clone the repository
Click on the Code button on the right on the forked repository
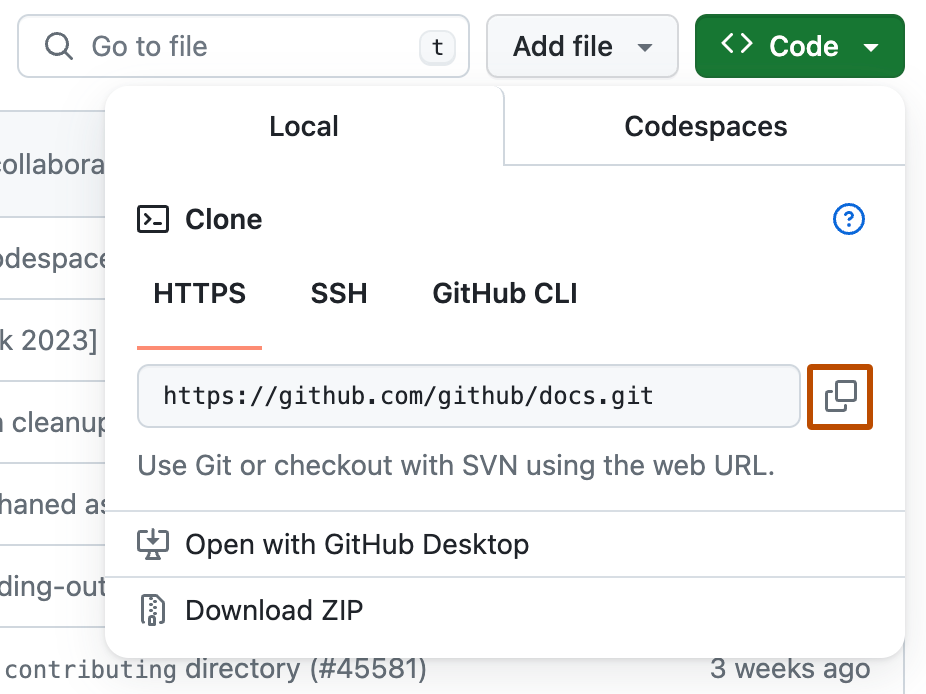
Copy the url to clone the repository using HTTPS
Open GitBash at your preffered working directory.
type
git clone, and then paste the URL you have copied earlier. for Example; If your username is HarryPotter the repository you have forked is hogwarts then the command looks likegit clone https://github.com/HarryPotter/hogwarts.gitPress
Enter. Your local clone will be created.Cloning into
hogwarts... \ remote: Counting objects: 10, done.\ remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done. \ remove: Total 10 (delta 1), reused 10 (delta 1) \ Unpacking objects: 100% (10/10), done.
You are good to start working on your project from your favourite Text Editor.
for setting up this project.. Look up here
Making and Pushing Changes into the repository.
Step 1: Create a branch in your repository before making any changes. A short, descriptive branch name enables your collaborators to see ongoing work at a glance. For example, add-code-of-conduct. For more information, see "Creating and deleting branches within your repository."
Step 2: Make changes. On your branch, make any desired changes to the repository.
For more information, see
- "Creating new files"
- "Editing files"
- "Renaming a file"
- "Moving a file to a new location"
- "Deleting files in a repository"
Step 3: Your branch is a safe place to make changes. If you make a mistake, you can revert your changes or push additional changes to fix the mistake. Your changes will not end up on the default branch until you merge your branch.
Step 4: Commit and push your changes to your branch. Give each commit a descriptive message to help you and future contributors understand what changes the commit contains. For example, fix typo or increase rate limit.
Creating a Pull Request
At last, you're ready to propose changes into the main project! This is the final step in producing a fork of someone else's project, and arguably the most important. If you've made a change that you feel would benefit the community as a whole, you should definitely consider contributing back.
Step 1:head on over to the repository on GitHub where your project lives. For this example, it would be at https://www.github.com/HarryPotter/hogwarts. You'll see a banner indicating that your branch is one commit ahead of main. Click Contribute and then Open a pull request.

Step 2: GitHub will bring you to a page that shows the differences between your fork and the main repository. Click Create pull request.
- In the "base branch" drop-down menu, select the branch of the upstream repository you'd like to merge changes into.
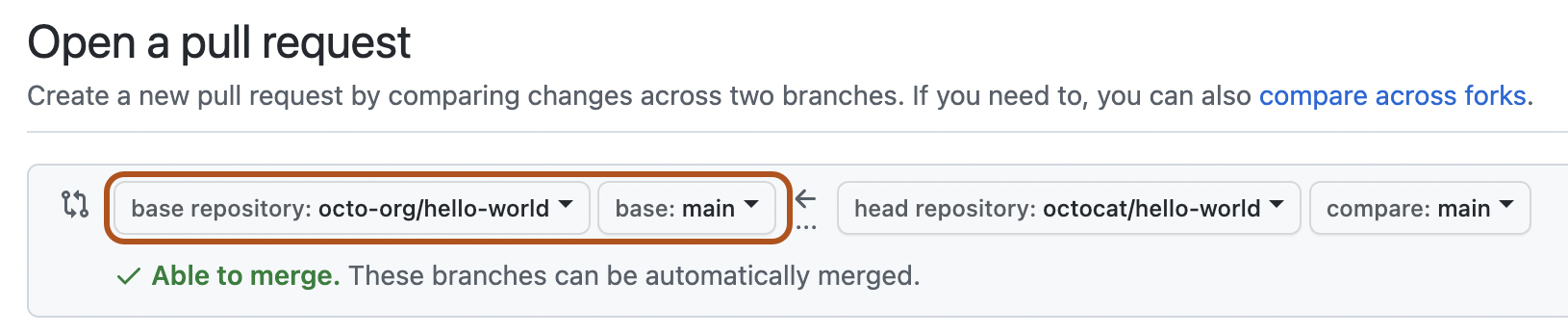
- In the "head fork" drop-down menu, select your fork, then use the "compare branch" drop-down menu to select the branch you made your changes in.

Step 3: GitHub will bring you to a page where you can enter a title and a description of your changes. It's important to provide as much useful information and a rationale for why you're making this pull request in the first place.
 Step 4:The project owner needs to be able to determine whether your change is as useful to everyone as you think it is.
Step 4:The project owner needs to be able to determine whether your change is as useful to everyone as you think it is.
Finally, click Create pull request.

Contribute in other ways
Opening an issue
Opening an issue in the following situations is feasable
- Report an error in the project
- discuss a upgrade or any new idea that can be implemented
- proposing a new feature or idea
Tips for Communicating a issue
- If you see an open issue that you want to tackle, comment on the issue to let people know you’re on it. That way, people are less likely to duplicate your work.
- If an issue was opened a while ago, it’s possible that it’s being addressed somewhere else, or has already been resolved, so comment to ask for confirmation before starting work.
- If you opened an issue, but figured out the answer later on your own, comment on the issue to let people know, then close the issue. Even documenting that outcome is a contribution to the project.
to learn more in detail, click here.
